1.单行文本溢出(部分浏览器需要加上高度)
1 | overflow: hidden; |
2.多行文本溢出
1 | overflow : hidden; |
上面方法合适WebKit浏览器或移动端(绝大部分是WebKit内核的)浏览器。
其他浏览器解决方案:
目前没有什么CSS的属性可以直接控制多行文本的省略显示,比较靠谱的办法应该就是利用相对定位在最后面加上一个省略号了,代码可以参考下面
1 | p { |
不过这样会有一点问题:
1)需要知道显示的行数并设置行高才行;
2)IE6/7不支持after和content,需要添加一个标签来代替;
3)省略号的背景颜色跟文本背景颜色一样,并且可能会遮住部分文字,建议可以使用渐变的png背景图片代替。
3. 纯css实现容器高度随着宽度等比例变化
1)利用一个隐藏图片来实现
假如你想要容器的宽高比是4:3,那就选一个宽高比正好是4:3的图片,把这个图片放到容器里。设置图片宽度100%,高度auto,那么图片会把这个容器撑开,正好撑开到4:3。然后可以隐藏这个图片。
1 | #container { |
如果你觉得增加img标签多发了http请求,那么你可以把图片变成base64格式,由于我们的图片没有实际显示作用,我们可以大胆压缩。所以既没有http请求,还可以让图片很小。
2)可以利用css3的calc函数.(利用第二种情况来实现)
第一种情况 position:absolute
如果元素是position:absolute的话,那么百分比基准是相对他父级元素中第一个position:relative元素的宽和高为基准的。
比如position:relative元素的width为200px,height为100px
那么position:absolute元素里
1 | width:calc(10%) // 20px |
第二种情况 普通文档流中元素
这种情况元素的宽和高的百分比基准都是父元素的宽度。
比如一个div的父元素宽度是200px,高度是100px.
这个div设置
1 | width:calc(10%) // 20px |
后来自己证实得知,calc函数不区分文档流和absolute元素
加入父元素宽为200px,高为100px
1 | width:calc(10%) // 20px |
对于宽和margin和padding值,百分比是基于父元素的宽度
对于高,百分比是基于父元素的高度
3)使用padding-bottom实现
padding-bottom属性值百分比是按照父容器宽度来计算的,所以所以这里我们设置容器宽度为父容器的50%;padding-bottom也为50%;就都是父容器宽度的50%;显示出来就是一个完美的正方形了
1 | <style type="text/css"> |
4) 利用canvas来固定容器宽高比(4:3)
1 | <div class="container"> |
4. 行高
1)line-height的含义
1 | line-height:26px; 表示行高为26个像素 |
2)line-height的继承性
(a)带单位的行高继承的是计算值(em,%都算是单位)。
如父元素的字体大小为14px,定义行高line-height:2em;则计算值为 28px,不会因其子元素改变字 体尺寸而改变行高。(例如:父元素14px,子元素12px,那么行高就是28px,子元素虽然字体是12px,行高还是父元素的行高)
(b)不带单位的行高是直接继承(数字),比如父容器line-height:2,那么子元素line-hieght也是2。
如父元素字体尺寸为14px,行高line-height:2;子元素字体为12px,不需要再定义行高,他默认的行高为24px。(例如:子元素12px,他的行高是24px,不会继承父元素的28px)
例子:
1 | <style> |
5.图片在容器里水平垂直居中
1 | position: absolute; |
适用场景:图片比容器小。
如果图片比容器大,则只会进行上下居中,左右不会居中。并且图片不会进行缩放,如果想要缩放,请自行设置height: 100% 或者width: 100%
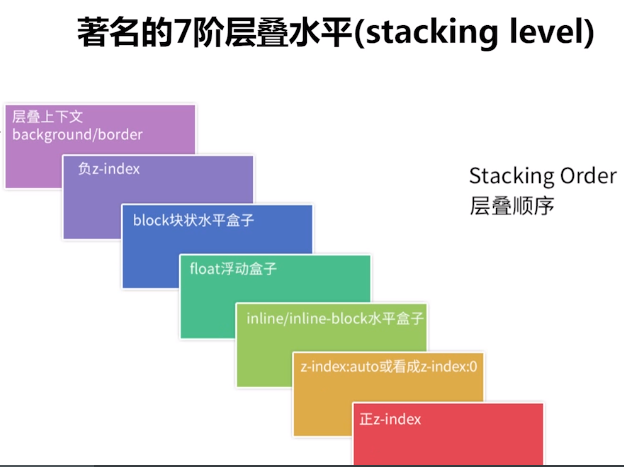
6. 层叠顺序
7. 滚动加载更多
在容器元素上加’list-wrapper-for-load’类,在内容元素上加’list-content-for-load’
注意:容器元素必须固定高度,并且 设置overflow: auto或者overflow:scroll, 否则无法触发滚动事件
1 | import Vue from 'vue'; |
8.光标下划线跟随效果
1 | <ul> |
1 | ul { |

9. 页面内容不足一屏幕,footer处于窗口底部 ;页面内容超过一屏幕,footer处于页面底部。
1 | <html> |
关键点在于:虽然content里面的元素高度不确定,但是设置content的min-height为100%;在content的父元素上加一个after伪元素(其实就是加一个和content同级的兄弟元素。如果底部元素很多,不太方便用after那就直接在content后面加一个div,也是一样的 原理;如果底部元素简单,直接只用after可以让元素层级更简单);同时让content有一个padding-bottom来给底部元素让位,底部元素设置一个margin-top为负数,这样底部元素自身就网上移动了。
10. border-radius 与overflow 问题
第一部分:问题由来:
1 | <div class="wrapper"> |
1 | .wrapper { |
当外层div需要一个圆角时,需要设置overflow:hidden来遮盖里面content类的超出圆角部分的内容。
如果content类的内容很少,不需要滚动的时候上面的写法没有问题。但是当content类的内容很多,需要滚动展示的时候,设置overflow: hidden; 就会不能滚动,所以需要写成overflow: auto;
然而你会发现写成overflow: auto; 之后border-radius: 6px;就不生效了,圆角看不见了。这时候需要用到mask-image 属性。遮罩图片是一张1px的全黑图片。
最终css长这样:
1 | .wrapper { |
第二部分:mask-image解析
mask-image即遮罩,就是在原始内容基础上只显示遮罩图片透明的部分(透明:没有,黑色:透明,白色:不透明,其它:介于两者之间)